Other GHGs are carbon monoxide, fluorinated gases, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), black carbon (soot), and brown carbon Among the greenhouse gases, only water vapour can absorb both incoming (UV) and outgoing (infrared) radiation Global WarmingCarbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), Ozone (O 3 ), and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), along with water vapour are known as greenhouse gases Due to human intervention, the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has increased remarkably causing the greenhouse effect Greenhouse Gases NamesNotes of Ch 14 Science Class 9 Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases like methane, carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide are present in the atmosphere to stop the heat falling on the Earth and not absorb it Hence, this keeps it warm and this phenomenon is called the greenhouse effect That is how Science Class 9 Chapter 14 notes help you to get to

Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples
Greenhouse gases chart ncert
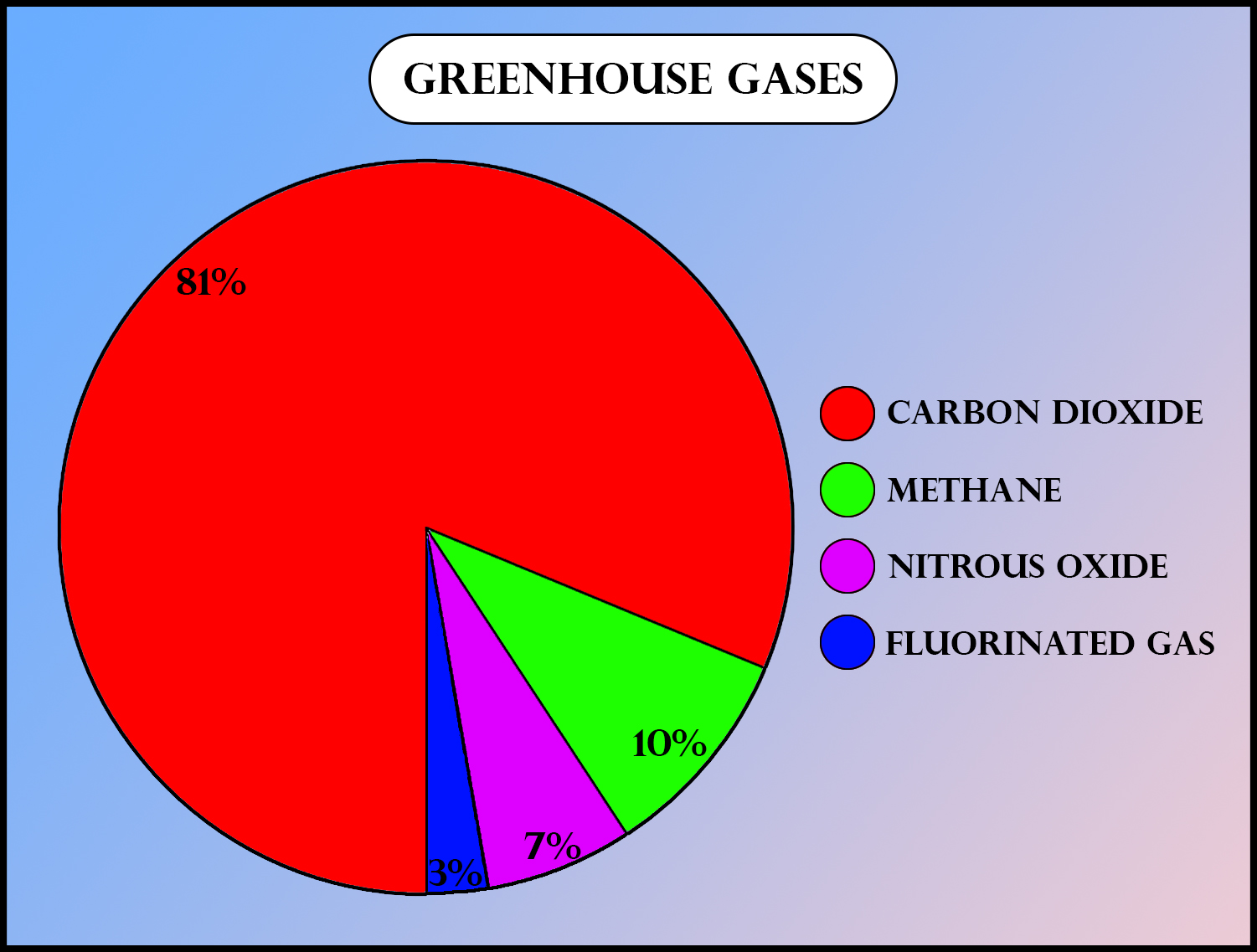
Greenhouse gases chart ncert-Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedGreenhouse gases refer to the sum of seven gases that have direct effects on climate change carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) The data are expressed in CO 2 equivalents and refer to gross direct emissions



India Needs Better Greenhouse Gases Emission Control Strategies The Federal
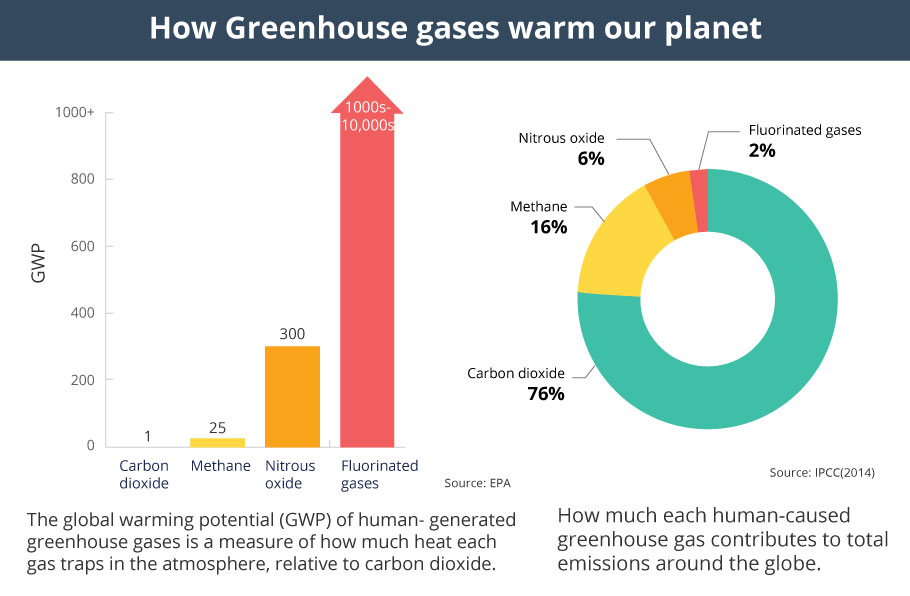
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) include carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, and fluoride gases These molecules in our atmosphere are called greenhouse gases Some of these gases may not be present in our atmosphere, but they can have a profound effect Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 314 Watts for every square meter of Earth's surface Just over 80 percent of that is due to carbon dioxide (66%) and methane (16%)Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents
4 Nitrous Oxide By far the most fast and furious of the greenhouse gases, nitrous finds uses in rocket fuel, making cars more awesome, Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They letAnd ozone, which causes 3–7 percentThe issue is how the strength of the greenhouse effect changes when human activity increases the atmospheric
The most significant greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour (Surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases also trap infrared radiation to a lesser extent) While making up just a fraction of all atmospheric gases, greenhouse gasses have a profound influence on the Earth system's energy budgetGreenhouse gas emissions increased 70 percent between 1970 and 04 Emissions of carbon dioxide, the most important greenhouse gas, rose by about 80 percent during that time The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere today farView Chris Schacht's profile on LinkedIn, the world's largest professional community Chris has 1 job listed on their profile See the complete profile on LinkedIn and discover Chris




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Charting Transport




Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Biology Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion And Deforestation
Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeApplications of Inert Gases There are numerous uses of inert gases or noble gases in various fields specially in the field of metallurgy Here we are listing few applications of each inert gas separately in many fields – Helium Helium is used for the treatment of asthma, emphysema and other breathing problems Helium is used in balloons Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) cooler



Utanzas Huz Kedvezmeny Composition Of Air Pie Chart Alfonsoalfonso Com




Relative Contribution Of A Various Greenhouse Gases And B Various Download Scientific Diagram
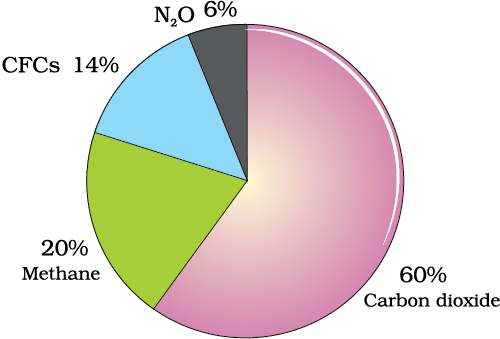
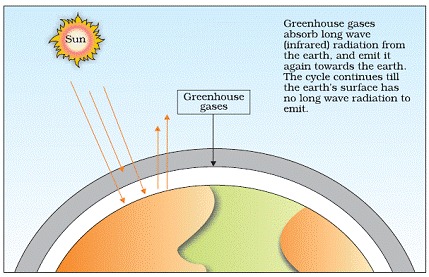
Greenhouse effect is the phenomenon responsible for heating of the earth due to the presence of certain gases in the atmosphere Greenhouse gases (C0 2 CH 4 N 2 0 and CFCs) allow the solar radiations to enter, but prevent the escape of heat radiations of longer wavelength When these greenhouse gases increases4n concentration in the atmosphere, global warming 2 Mars has a very thin atmosphere, nearly all carbon dioxideBecause of the Red Planet's low atmospheric pressure, and with little methane or water vapor to reinforce the weak greenhouse effect (warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from the planet toward space), Mars' surface remains quite cold, the average surface temperature being aboutCarbon dioxide is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide It is one method of reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere with the goal of reducing global climate change




Conventional Sources Of Energy Class Ten Science Ncert




Pin By Ncert Solutions On Cbse Tuts Photosynthesis Chapter 13 Biology
Top Ten Places That Emit Greenhouse Gases Created with Highcharts 901 Emissions in 17 (millions of metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent) Chart title China United States India European Union (27) Russia Indonesia Brazil Japan Iran South Korea 0 2k 4k 6k 8k 10k 12k 14k World101 Council on Foreign Relations CFRorg US Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Gas, 1990–19 This figure shows emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and several fluorinated gases in the United States from 1990 to 19 For consistency, emissions are expressed in million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents * HFCs are hydrofluorocarbons, PFCs are perfluorocarbons, SF6 is sulfurCarbon footprint, amount of carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions associated with all the activities of a person or other entity (eg, building, corporation, country, etc)It includes direct emissions, such as those that result from fossilfuel combustion in manufacturing, heating, and transportation, as well as emissions required to produce the electricity associated with goods and services consumed



Carbon Cycle And The Earth S Climate




Fluorinated Gases Wikipedia
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science (Python) NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science Greenhouse gases The most important anthropogenic effect on the climate is the increasing trend in the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere which is likely to cause global warming The graphic paints a picture of how that looks for each country China's emissions for energy alone make up nearly percent of total global discharge of greenhouse gasesIdentify three greenhouse gases identify two causes of global warming identify two effects of global warming identify four possible solutions to global warming conduct a "green audit" of his/her household (see Handout One) list three changes that can be made within the household to help combat global warming (see Handout One)



Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World




Relative Contribution Of Various Green House Gases T Biology
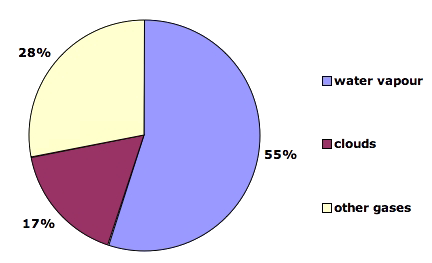
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesLet's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Methane (CH 4) Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) References and Resources This is indeed the greenhouse gas that is currently producing the greatest impact on the Earth's rapidly changing climate But it is far from the only one making its mark, and for mitigating climate change it's important to be able to compare the effects of the various gases that contribute to warming the planet



Environmental Issues Class 12 Notes Biology Mycbseguide Cbse Papers Ncert Solutions




Pdf Natural Gas Makes No Contribution To Climate Protection
Online classes for class 5 Watch the animated video, NCERT Solutions, Online tuition, and Download the CBSE Class 5 worksheets for All Subjects The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,Methane (CH 4), which causes 4–9 percent;



Sections
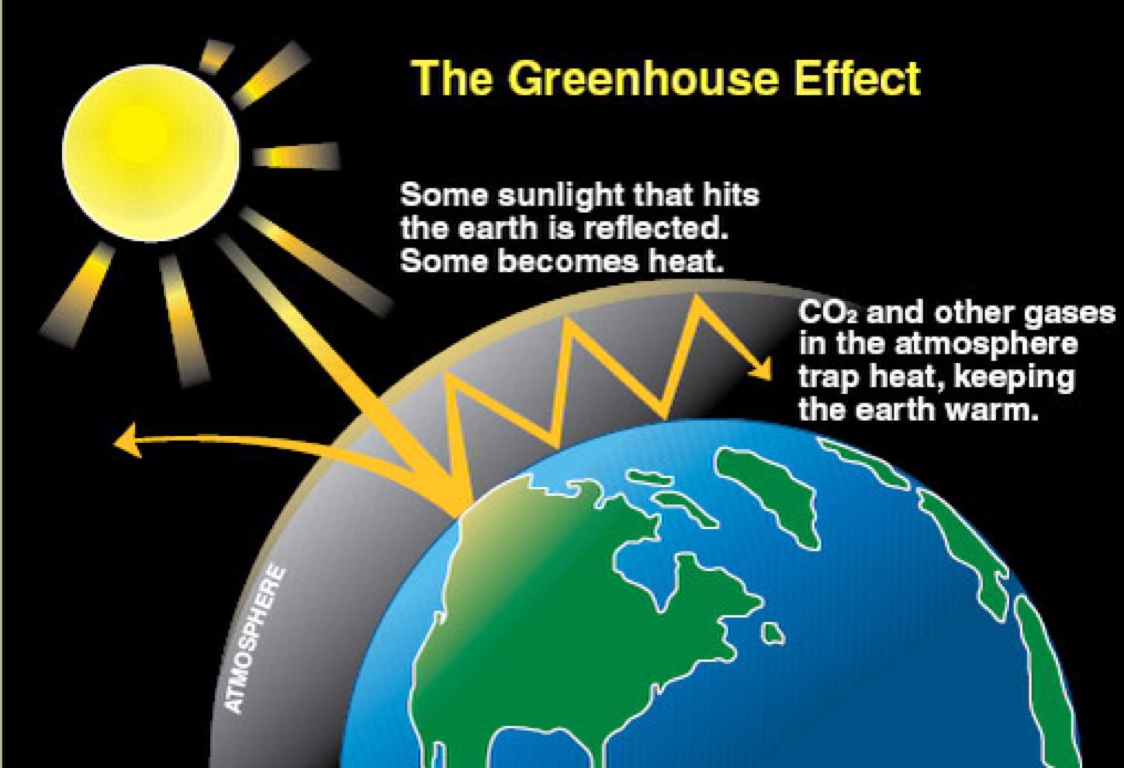



What Is The Difference Between The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Socratic
Burning coal, oil and natural gas (fossil fuels) – is a critical greenhouse gas Greenhouse gases absorb and retain heat from the sun Examples of greenhouse gases include methane, ammonia, sulfur dioxide and certain chlorinated hydrocarbons Many scientists believe that the build up of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can cause globalThe percentage composition of producer gas is discussed below Carbon dioxide = around 3% Hydrogen gas = 10 % to 15 % Carbon monoxide = 22 % to 30 % Nitrogen gas = 50 % to 55 % Noncombustible gases form the major portion of the producer gas The large portion of noncombustible gas results in a high calorific valueGreenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere




Pdf Policy Analysis Reveals The Need For New Approaches




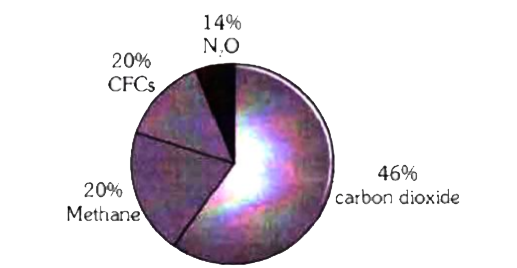
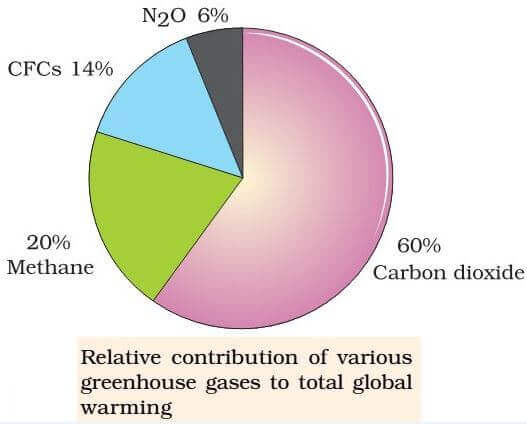
Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Various Greenhouse Gases To Total Global Warming Identify The Gases P Q R And S Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xii C16 Ei E01 074 Q01 Png
Carbon dioxide (CO 2), which causes 9–26 percent;On Earth, the major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 36–70 percent of the greenhouse effect (not including clouds);Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Graphing Tool Interactive Data Visualization Tool The Interactive Data Visualization tool gives users a way to explore the abundance of different gases at more than 0 sampling sites around the world You can view graphs showing how the amount of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and various
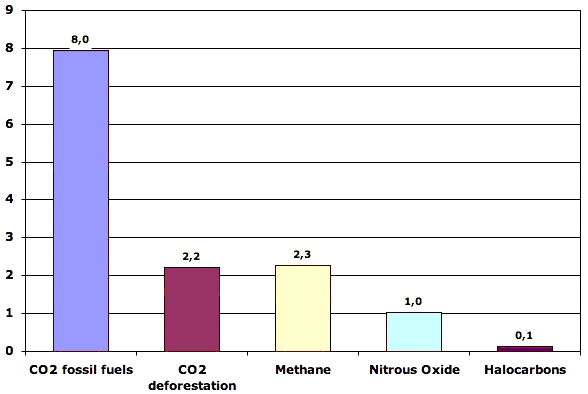



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Ncert Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 14 Sources Of Energy
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities In 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)Greenhouse Gases Examples The Primary GHGs are Water Vapour;View Abhishek Rathan Kumar's profile on LinkedIn, the world's largest professional community Abhishek Rathan has 6 jobs listed on their profile See the complete profile on LinkedIn and




A Pie Chart Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions



Ncert Solutions For Class 9 English Main Course Book Unit 3 Environment Chapter 2 Save Mother Earth
Greenhouse gases warm the planet Scientists know with virtual certainty that increasing greenhouse gas concentrations tend to warm the planet In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over timeGlobal Warming and Greenhouse Effect About 75 % of the solar energy reaching the earth is absorbed by the earth's surface, which increases its temperature The rest of the heat radiates back to the atmosphere Some of the heat is trapped by gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, chlorofluorocarbon compounds (CFCs) and water vapour in theAAPG COSUNA chart (1985) Midland Basin (Reed and Mazzullo, 1987) Midland Basin Fusulinid zonation Wolfcamp Formation Eastern Shelf Lower Strawn Limestone = Early Strawn Middle & Upper Strawn = lower portion of WC D STRAWN GROUP STRATIGRAPHY (DESMOINESIAN SERIES) Wolfcampian Admiral Fm Putnam Fm Moran Fm Pueblo Fm Cisco – Canyon Group Gp



Greenhouse Gas In Atmosphere Ias Gatewayy



1 Details Of Module And Its Structure Module Detail Subject Name Geography Course Name Geography 01 Class Xi Semester 1 Mo
To prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to




Utanzas Huz Kedvezmeny Composition Of Air Pie Chart Alfonsoalfonso Com



Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World
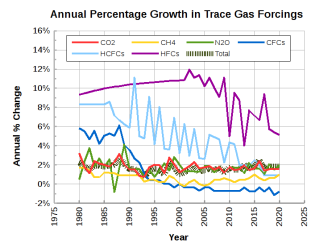



Fluorinated Gases Wikipedia




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




Energy Consumption In Average Australian Household Band 8 Ielts Report Sample Ielts Practice Org



1




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Ncert Class Viii Science Solutions Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Part 2 Flexiprep




The Figure Shows Relative Contributions Of Various Green House Gases To The Total Global Warming I Name The Gases A And B Ii Explain How Increase In Green House Gases In Earth S Atmosphere
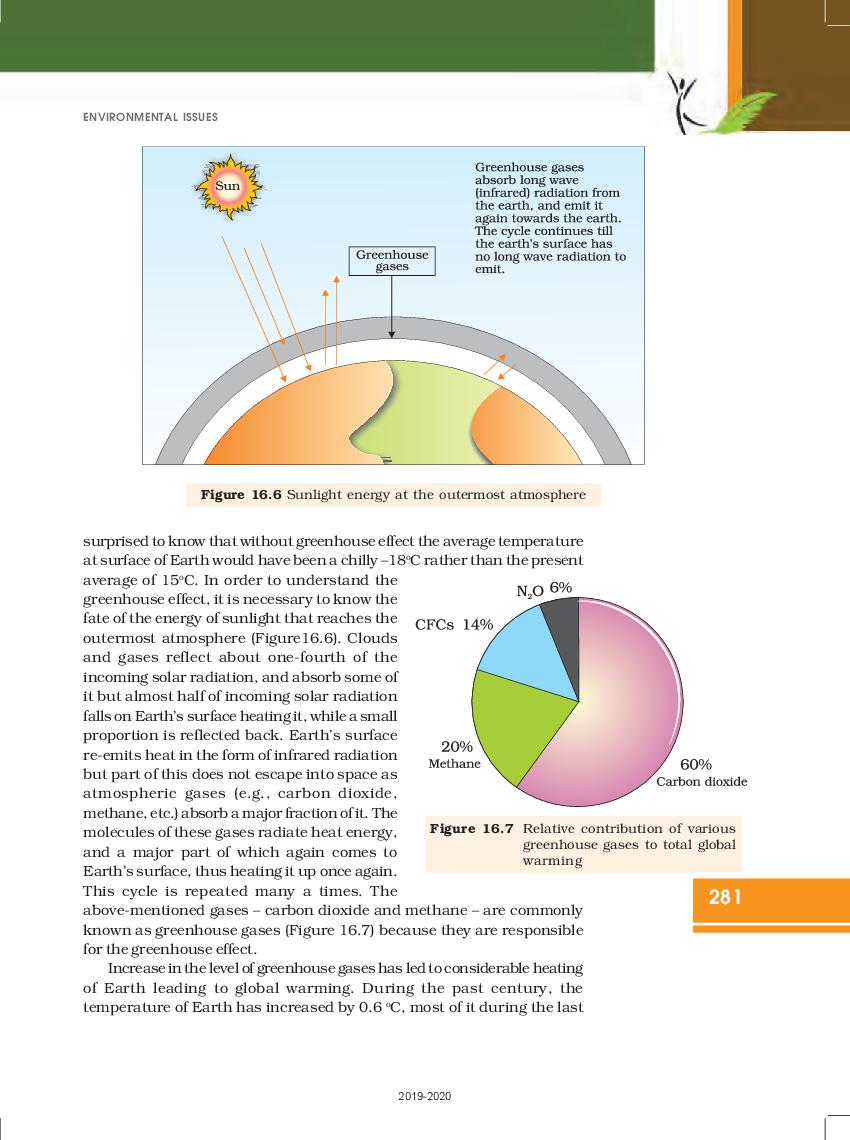



Ncert Book Class 12 Biology Chapter 16 Environmental Issues Aglasem Schools




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube



2




Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Various Greenhouse Gases To Total Global Warming Identify The Gases P Q R And S Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xii C16 Ei E01 074 Q01 Png



Ozone Depletion



Simple




Environment And Ecology Quiz For Ias Prelims




Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World




The Relative Contribution Of Various Green House Gases To To
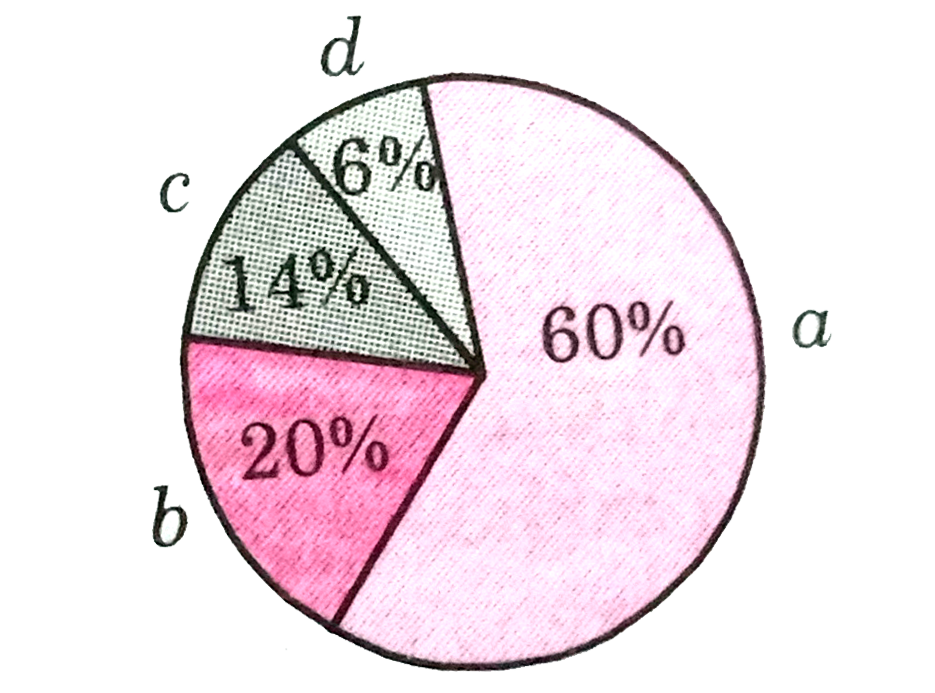



Relative Contribution Of Various Green House Gases To Total Global Warming Is Given In The Diagrams Identify The Green House Gases Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Din Obj Bio V03 C38 E01 521 Q01 Png Width 80




Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Va




Revision Notes For Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources Class 9th Askiitians




Hydroelectric Power Plant Class 10 Science Notes Teachoo




India Needs Better Greenhouse Gases Emission Control Strategies The Federal




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Concepts Videos And Examples




Climate Change Performance Index




Greenhouse Effect Meaning Consequences And Impact Teachoo




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Concepts Videos And Examples




Motion And Time With Images Time Diagram Distance Time Graphs Motion




Global Warming
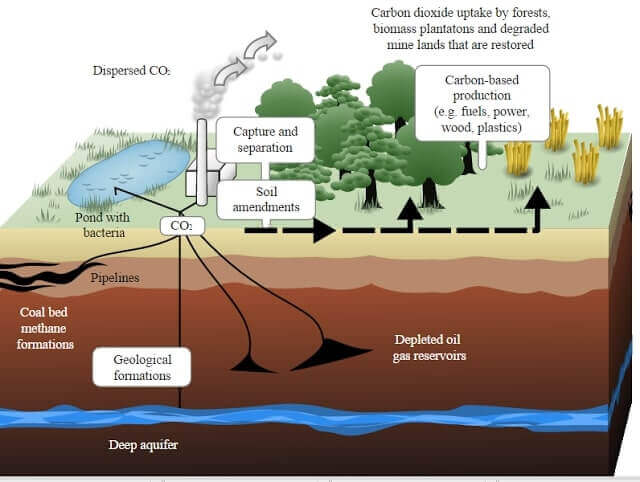



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias



Greenhouse




Current Affairs Changing Land Use Pattern And Climate Change Perfect 7 Weekly Magazine April 19 Issue 2 Dhyeya Ias Best Upsc Ias Cse Online Coaching



Official Language Policy As A Factor In Using Receptive Multilingualism Among Members Of An Estonian And A Finnish Student Organization Springerlink




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Charting Transport




Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Various Greenhouse Gases To Total Global Warming Identify The Gases P Q R And S




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples



Environmental Issues Class 12 Notes Biology Mycbseguide Cbse Papers Ncert Solutions




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples




Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Various Greenhouse Gases To Total Global Warming Identify The Gases P Q R And S Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xii C16 Ei E01 074 Q01 Png




Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Biology Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion And Deforestation




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



The Figure Below Shows The Relative Contribution Of Four Greenhouse Gases To Global Warming I Identify The Gases A And C Ii Why Are These Four Gases C Biology Topperlearning Com




Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Geography Social Science Chapter 4 Air Indianexpresss In



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Class 12 Biology Cbse



Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Various Greenhouse Gases To Total Global Warming Identify The Gases P Q R And S Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xii C16 Ei E01 074 Q01 Png




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples
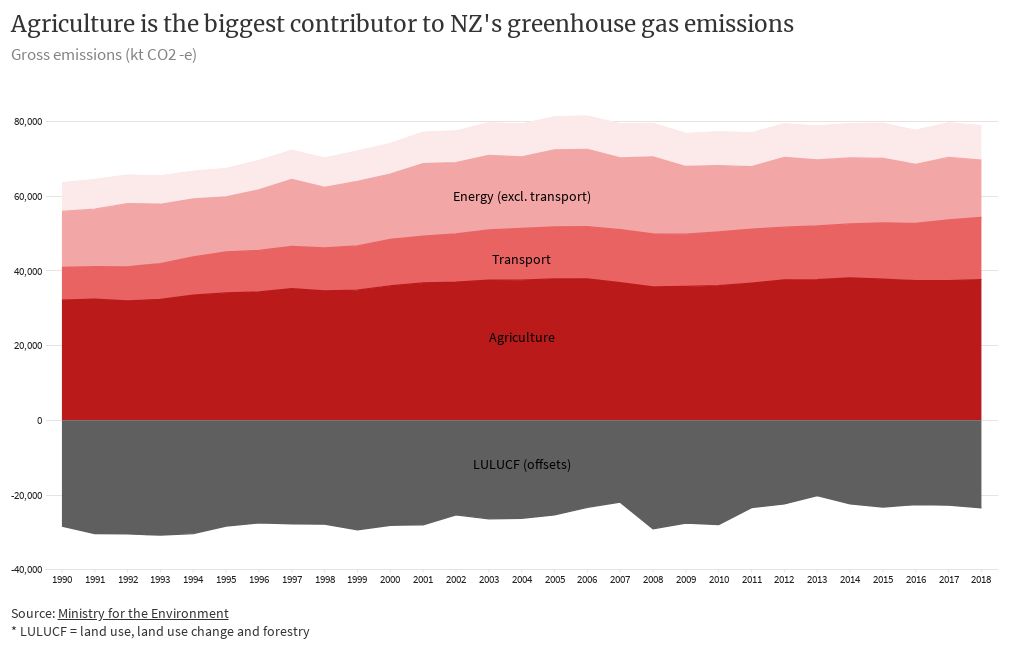



Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World
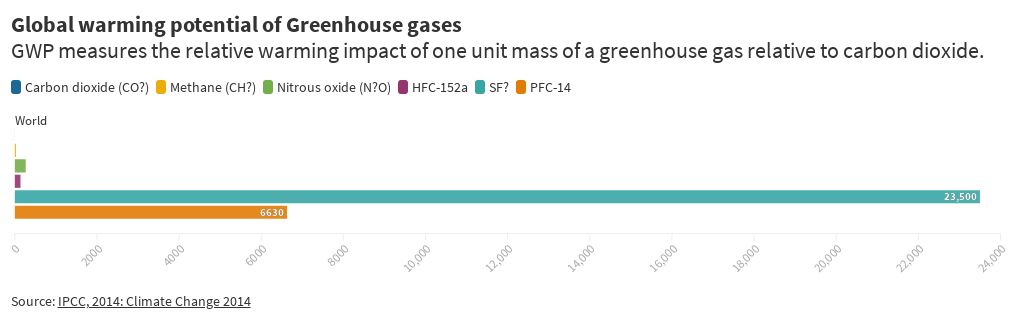



Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World



Study The Following Pie Chart Carefully It Lists The Various Sectors Responsible For Gas Emissions Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Ncert Class Viii Science Solutions Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Part 2 Flexiprep




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Charting Transport




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
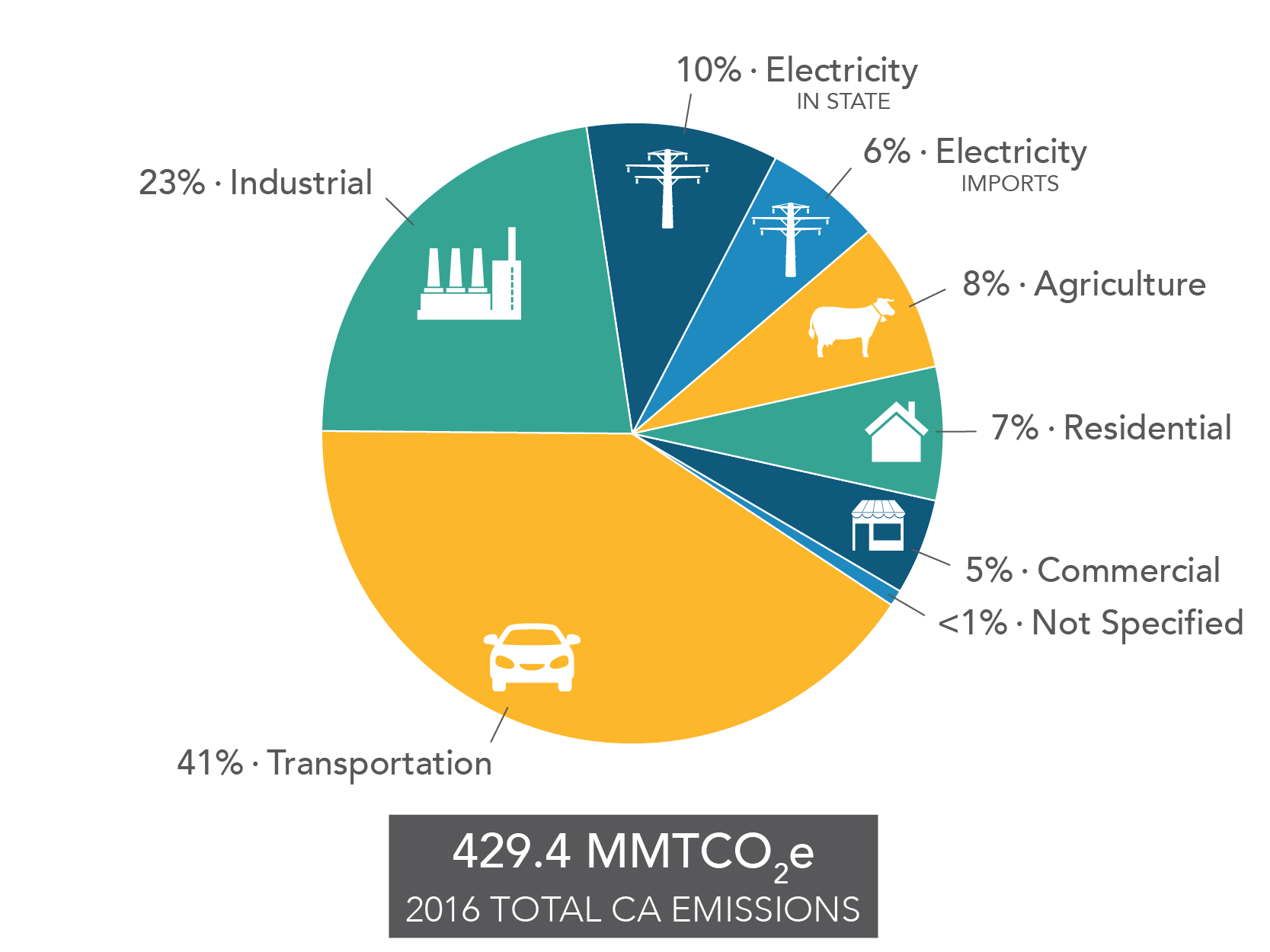



Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World
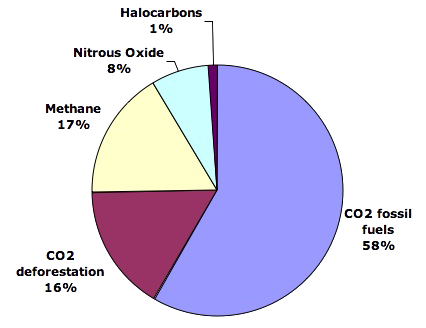



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



1 Details Of Module And Its Structure Module Detail Subject Name Geography Course Name Geography 01 Class Xi Semester 1 Mo




Global Warming Pie Chart 35 Images Ontario To Spend 7 Global Warming Glaciers The Water Towers Of The World



Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Carbon Sequestration Pmf Ias




How To Decarbonize America And The World Techcrunch Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gas Emissions Global Warming




Revision Notes For Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Class 8th Askiitians




Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases With Examples



Greenhouse Gas In Atmosphere Ias Gatewayy




Long Answer Question What Is Greenhouse Effect Name The Different Greenhouse Gases Snapsolve
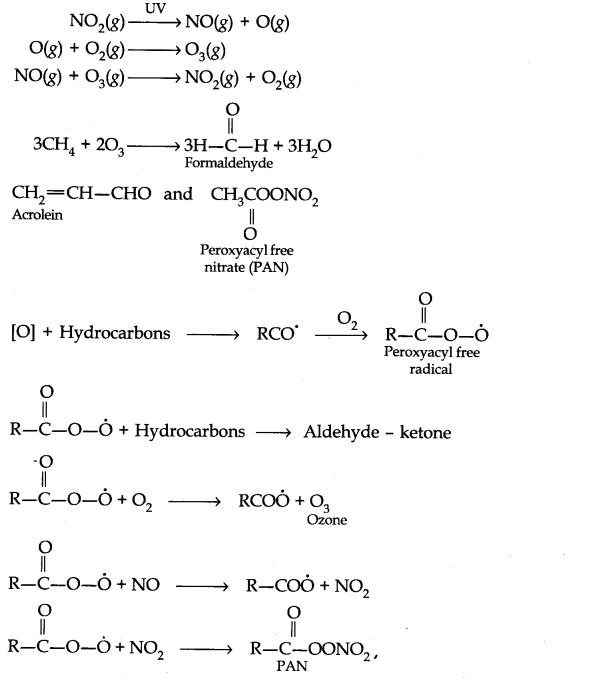



Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Learncbse In
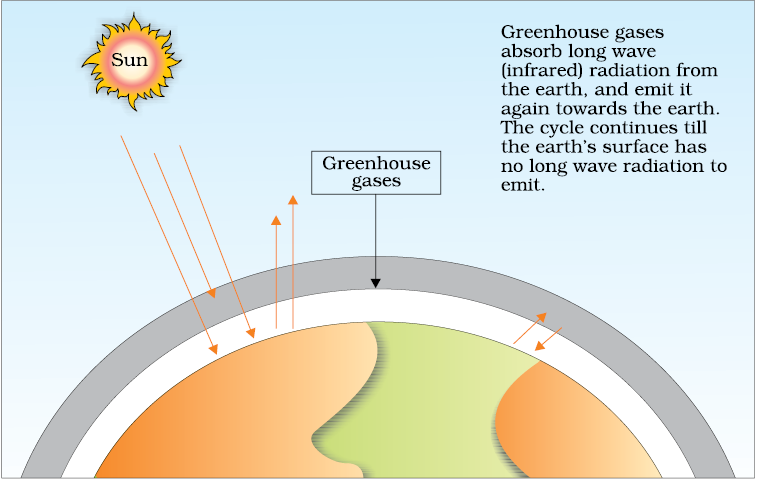



Sections




Given Pie Diagram Represents The Relative Contribution Of Various Greenhouse Gases To Total Global Warming Identify The Gases P Q R And S Img Src D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xii C16 Ei E01 074 Q01 Png




Indiscriminate Human Activities Have Strengthened The Greenhouse Effect Resulting In Global Warming Give The Relative Contribution Of Various Biology Environmental Issues Meritnation Com




Revision Notes For Science Chapter 18 Pollution Of Air And Water Class 8th Askiitians



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Q8 Describe The Green House Ef Lido
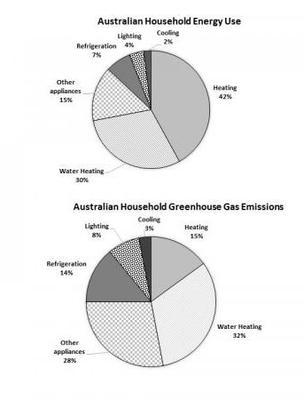



Australian Household Energy Consumption Task 1 Academic Ielts Report Sample Ielts Practice Org




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Essay On Greenhouse Effect On Impact Of Global Warming On Oceans For Students And Children In English A Plus Topper



2
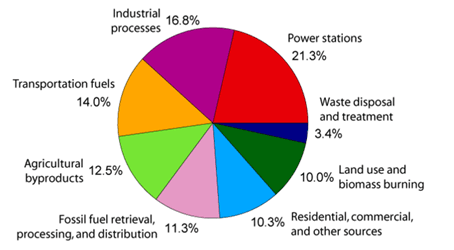



Greenhouse Gases Ghgs Gktoday




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Charting Transport




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Important Questions For Cbse Class 12 Biology Greenhouse Effect Ozone Depletion And Deforestation




Environmental Effects Of Aviation Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿